The Science Behind Face Whitening Creams: How They Work?
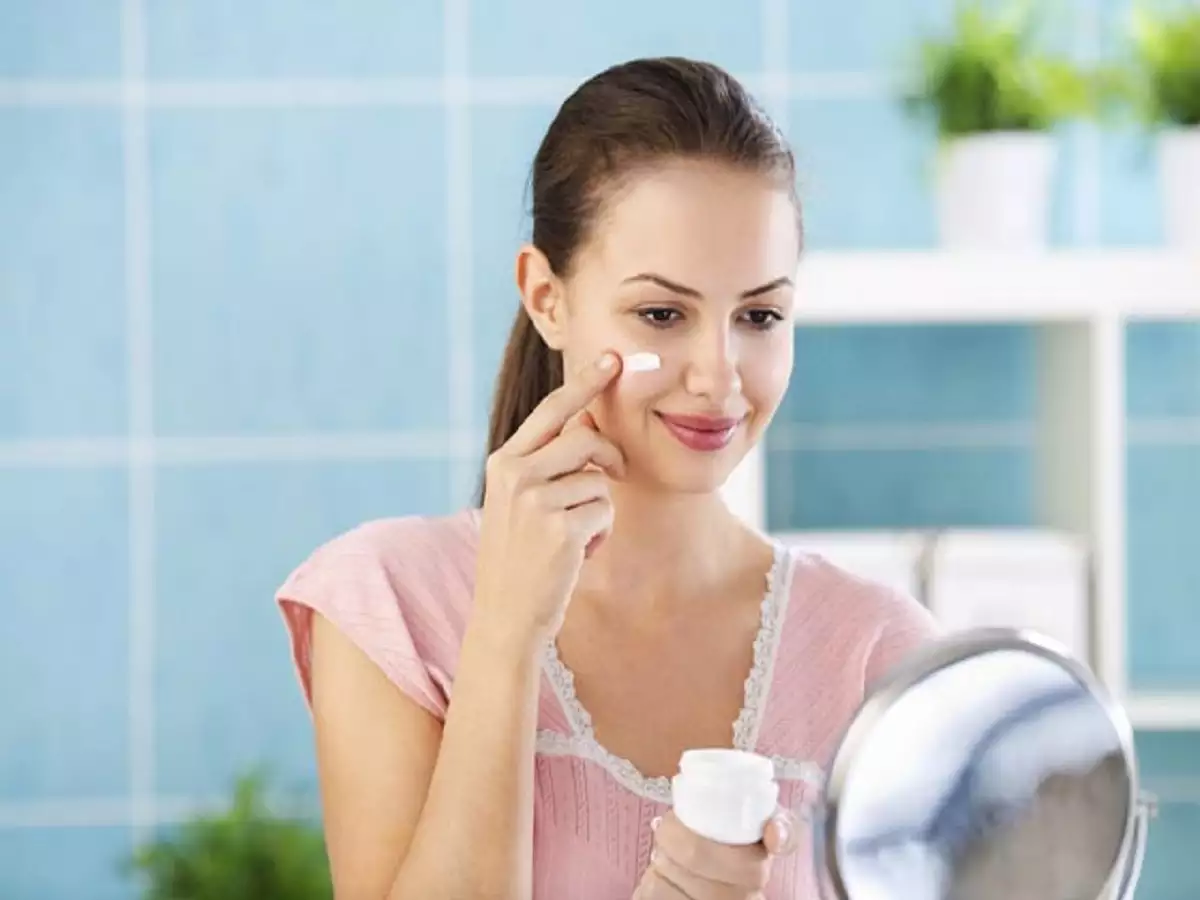
Face whitening creams have become increasingly popular in recent years, as people look for ways to achieve a brighter and more even complexion. The science behind these products is complex and multifaceted, but understanding the key ingredients and mechanisms can help you choose the right face whitening cream for your skin type and concerns.
The first step in the process of skin lightening is the reduction of melanin production. Melanin is the pigment responsible for giving color to your skin, hair, and eyes. When exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light, skin cells called melanocytes produce more melanin to protect the skin from the harmful effects of the sun. This results in darker, sun-tanned skin. Face whitening creams work by inhibiting the production of melanin, or reducing the amount of melanin that is produced, to lighten the skin.
One of the most common ingredients used in face whitening creams is hydroquinone. Hydroquinone is a chemical that blocks the production of melanin by inhibiting the enzyme tyrosinase, which is responsible for the synthesis of melanin. When applied topically, hydroquinone lightens the skin by reducing the amount of melanin produced. However, hydroquinone has come under scrutiny in recent years due to concerns about its safety and potential side effects, including skin irritation and, in rare cases, permanent discoloration. As a result, some countries have banned or restricted the use of hydroquinone in cosmetics.

Another popular ingredient used in face whitening creams is kojic acid. Kojic acid is derived from a type of fungus and is commonly used as a natural alternative to hydroquinone. Like hydroquinone, kojic acid works by inhibiting the production of melanin, but it is less likely to cause skin irritation.
In addition to reducing melanin production, face whitening creams can also work by reducing the transfer of melanin from melanocytes to surrounding skin cells. This process is known as melanosome transfer, and it is responsible for the even distribution of melanin in the skin. Inhibiting melanosome transfer can help to prevent dark spots, discoloration, and hyperpigmentation. Ingredients such as arbutin, bearberry extract, and licorice root extract have been shown to be effective in reducing melanosome transfer and lightening the skin.
Finally, some face whitening creams work by exfoliating the skin to remove dead skin cells and reveal brighter, smoother skin. Ingredients such as glycolic acid, lactic acid, and salicylic acid are commonly used in face whitening creams to gently exfoliate the skin and improve the appearance of dark spots, discoloration, and hyperpigmentation. These ingredients help to unclog pores, remove dead skin cells, and brighten the skin.
It is important to choose a face whitening cream that is formulated for your skin type and concerns. If you have dry or sensitive skin, it is best to avoid products that contain harsh ingredients, such as hydroquinone, that may cause skin irritation. Instead, look for products that contain gentler ingredients, such as kojic acid, arbutin, or glycolic acid.
If you have dark spots or hyperpigmentation, it is best to choose a face whitening cream that contains ingredients that can reduce melanin production, such as hydroquinone or kojic acid, as well as ingredients that can reduce melanosome transfer, such as arbutin or bearberry extract.
The science behind face whitening creams is complex and involves reducing melanin production, inhibiting melanosome transfer, and exfoliating the skin. The key ingredients in these products include hydroquinone, kojic acid, arbutin, bearberry extract, licorice root extract, glycolic acid, lactic acid, and salicylic acid. These ingredients work together to lighten the skin and improve the appearance of dark spots, discoloration, and hyperpigmentation.

It is important to choose a face whitening cream that is formulated for your skin type and concerns, and to use it as directed to avoid skin irritation and potential side effects. In addition, it is important to protect your skin from the sun, as UV exposure can trigger the production of melanin and undo the benefits of face whitening creams. Use a sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, and reapply it every two hours when spending time outdoors.
In conclusion, the science behind face whitening creams is fascinating and complex, and understanding the key ingredients and mechanisms can help you choose the right product for your skin type and concerns. Whether you are looking to achieve a brighter, more even complexion or to improve the appearance of dark spots and hyperpigmentation, face whitening creams can be a safe and effective way to achieve your skin goals. Just be sure to choose a product that is right for you, and use it as directed to achieve the best results.
February 8, 2023